- 3 Posts
- 20 Comments

 3·5 months ago
3·5 months agocurrently, yes, but this is more an investigation into how well a neural network could play a bullet hell game
very few bullet hell AI programs rely on machine learning and virtually all of the popular ones use algorithms.
but it is interesting to see how it mimics human behaviour, skills and strategies and how different methods of machine learning perform and why
(plus I understand machine learning more than the theory behind those bullet hell bots.)

 1·5 months ago
1·5 months agothe training environment is pretty basic right now so all bullets shoot from the top of the screen with no enemy to destroy.
additionally, the program I’m using to get player and bullet data (twinject) doesn’t support enemy detection so the neural network wouldn’t be able to see enemies in an existing bullet hell game. the character used has a wide bullet spread and honing bullets so the neural network inadvertently destroys the enemies on screen.
the time spent in each training session is constant rather than dependent on survival time because the scoring system is based on the total bullet distance only.

 1·5 months ago
1·5 months agodefinitely. usually algorithms are used to calculate the difficulty of a game (eg. in osu!, a rhythm game) so there’s definitely a practical application there

 3·5 months ago
3·5 months agoone problem ive seen with these game ai projects is that you have to constantly tweak it and reset training because it eventually ends up in a loop of bad habits and doesnt progress
you’re correct that this is a recurring problem with a lot of machine learning projects, but this is more a problem with some evolutionary algorithms (simulating evolution to create better-performing neural networks) where the randomness of evolution usually leads to unintended behaviour and an eventual lack of progression, while this project instead uses deep Q-learning.
the neural network is scored based on its total distance between every bullet. so while the neural network doesn’t perform well in-game, it does actually score very good (better than me in most attempts).
so is it even possible to complete such a project with this kind of approach as it seems to take too much time to get anywhere without insane server farms?
the vast majority of these kind of projects - including mine - aren’t created to solve a problem. they just investigate the potential of such an algorithm as a learning experience and for others to learn off of.
the only practical applications for this project would be to replace the “CPU” in 2 player bullet hell games and maybe to automatically gauge a game’s difficulty and programs already exist to play bullet hell games automatically so the application is quite limited.

 7·5 months ago
7·5 months agoI always find it interesting to see how optimization algorithms play games and to see how their habits can change how we would approach the game.
me too! there aren’t many attempts at machine learning in this type of game so I wasn’t really sure what to expect.
Humans would usually try to find the safest area on the screen and leave generous amounts of space in their dodges, whereas the AI here seems happy to make minimal motions and cut dodges as closely as possible.
yeah, the NN did this as well in the training environment. most likely it just doesn’t understand these tactics as well as it could so it’s less aware of (and therefore more comfortable) to make smaller, more riskier dodges.
I also wonder if the AI has any concept of time or ability to predict the future.
this was one of its main weaknesses. the timespan of the input and output data are both 0.1 seconds - meaning it sees 0.1 seconds into the past to perform moves for 0.1 seconds into the future - and that amount of time is only really suitable for quick, last-minute dodges, not complex sequences of moves to dodge several bullets at a time.
If not, I imagine it could get cornered easily if it dodges into an area where all of its escape routes are about to get closed off.
the method used to input data meant it couldn’t see the bounds of the game window so it does frequently corner itself. I am working on a different method that prevents this issue, luckily.

 3·5 months ago
3·5 months agoI did create a music NN and started coding an UNO NN, but apart from that, no

 8·5 months ago
8·5 months agoyeah, the training environment was a basic bullet hell “game” (really just bullets being fired at the player and at random directions) to teach the neural network basic bullet dodging skills

- the white dot with 2 surrounding squares is the player and the red dots are bullets
- the data input from the environment is at the top-left and the confidence levels for each key (green = pressed) are at the bottom-left
- the scoring system is basically the total of all bullet distances
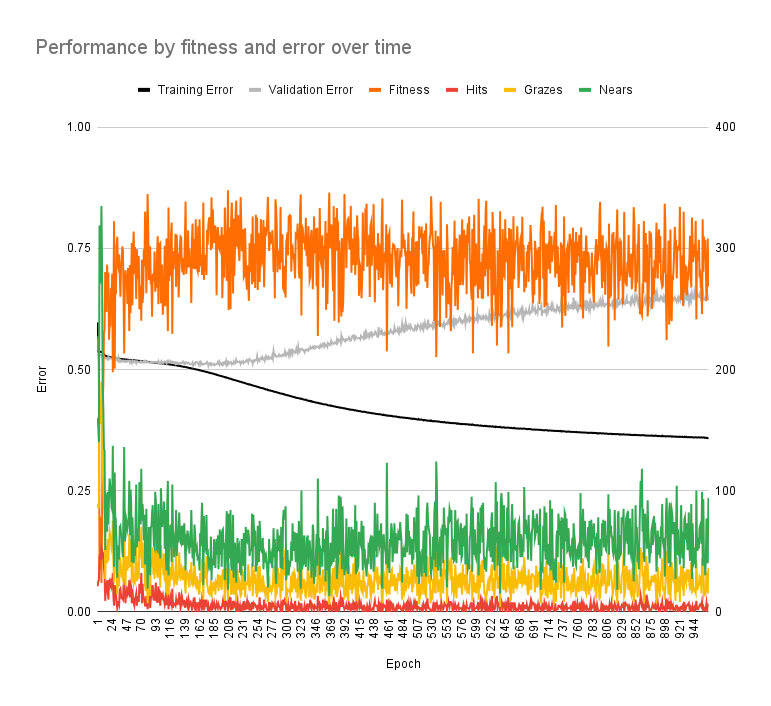
- this was one of the training sessions
- the fitness does improve but stops improving pretty quickly
- the increase in validation error (while training error decreased) is indicated overfitting
- it’s kinda hard to explain here but basically the neural network performs well with the training data it is trained with but doesn’t perform well with training data it isn’t (which it should also be good at)

 6·11 months ago
6·11 months agoFalling Lightblocks is a brilliant open-source Tetris clone for Android, with different gamemodes, multiplayer, leaderboards and a “campaign” mode. definitely worth your time

 1·1 year ago
1·1 year agoandroid only, but this app is great for time tracking. it does everything you list and much more, like individual activities that can be categorised, tags for activities, setting time goals, statistics to show time spent and streaks and so much more.
not sponsored but it really is worth a look
edit: also GPLv3 licensed

 1·1 year ago
1·1 year agothese simple type of ads used in the early internet was exactly the idea I was going for, having little involved to breach privacy or be used as an attack vector. more individual user ads was also what I was imagining, and looking at them, they are quite funny too

 2·1 year ago
2·1 year agoI'll just copy a previous reply:
the ads would ideally be limited to banners and gifs in the same style as these, with each user choosing whose ads they wish to host
no revenue or popularity (these are only for personal websites) would (hopefully) prevent users from hosting invasive ads. quite a few personal websites have banners linking to others, so this would be a more simpler approach
(although in principle, a whole project dedicated to automate this doesn’t sound good)>

 1·1 year ago
1·1 year agoah I see. thanks

 1·1 year ago
1·1 year agooh, ok. thanks

 1·1 year ago
1·1 year agomostly, but webrings seem closer

 1·1 year ago
1·1 year agoyeah, that sounds like a similar idea.
has anyone implemented this in a decentralised manner?

 2·1 year ago
2·1 year agoI'll try explain the idea more concisely:
- user wants to promote own website
- user creates ads (small banners and gifs) like these and hosts them on an instance of the software through their website
- the server-side implementation would have an API to fetch the URL of the advertisements from to embed to the website (just simple image files or gifs)
- user asks other people (friends, others in the fediverse) to save their website on these peoples' own lists of websites that they are willing to host the ads for
- people would host based off of similar content, interesting topics, and general goodwill as opposed to exposure (as very few personal websites get constant exposure to large audiences) and revenue (as this would be a willing move)
- the client-side implementation of those hosting other websites' ads would randomly pick a URL from the user's own list (similar to picking a random URL from a webring), use the API (something like /get_ad?) to retrieve the URL of a random ad from the promoting user and display that on their website
- "automatic" was a bad word choice, I'll change it now
- this wouldn't solve a problem, just automate the functions of webrings by giving every user their own decentralised "webring" (the list of websites) and displaying user-curated ads (probably at the bottom of the page where most banners are) as opposed to randomly picking from a webring
- those using personal websites would be the users, while visitors would be the audience.
should've made the wording more clearer in the post, my bad I guess. and to clarify, this is just an concept I thought about though and I don't actually have plans to develop this. (I've also edited the post with my final opinion on the subject.)

 1·1 year ago
1·1 year agothe ads would ideally be limited to banners and gifs in the same style as these, with each user choosing whose ads they wish to host
no revenue or popularity (these are only for personal websites) would (hopefully) prevent users from hosting invasive ads. quite a few personal websites have banners linking to others, so this would be a more simpler approach
(although in principle, a whole project dedicated to automate this doesn't sound good)

 1·1 year ago
1·1 year ago- people would choose individual websites (likely their friends) to host ads of, although list making would be problematic
- ideally would just serve images or gifs with as simple an API as possible
- similar idea to point 1 but abuse of such a system would be an issue (eg. a website is hacked and changed to inappropriate ads). one of the concept's main implications
- similar idea to point 2: videos could also be problematic though
- potentially some form of client-side (website) caching? this whole thing is just an idea, so I really don't know how it work
- no revenue - and therefore breaches of privacy and tracking would be unlikely - as the servers would be individually hosted, and therefore decentralised. however, this approach would make it significantly easier for malicious parties to pay users for ads.
- as to whether or not that happens would be the user's decision, although (at least right now) such advertising sounds more costly and hard to enforce.
- you're right that ad-blockers could (although probably not at first) be used to block ads, as the ads would be for other personal websites (no real ad protection needed as per point 6), some could unblock them knowing that they would be more ethical (again, just a concept). this would be a problem though as most visitors would have an ad-blocker regardless.
thanks for the points

 1·1 year ago
1·1 year agoyou're right that abuse would be the biggest issue, made worse if people host ads for many people. ideally people would naturally host few ads in a similar fashion to smaller instances (ideally) federating with few instances? also didn't realise that so many webrings still exist until I searched them up
Gentoo